Drop by the Chicago Botanic Garden’s Lenhardt Library to see rare book illustrations of hand-colored orchids in Asia that give a new perspective to Asia in Bloom: The Orchid Show.
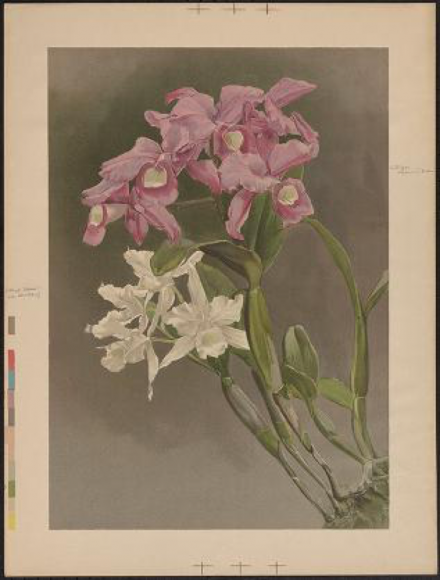
Of all the rare orchid books in the library’s collection, it’s a challenge to select illustrations for an exhibition to complement the Garden’s annual Orchid Show. Since the Orchid Show is so colorful, featuring 10,000 orchids in bloom, we usually try to showcase things that really pop. And although there are some extraordinarily colored illustrations in the library’s free rare books exhibition Asian Orchids Illustrated, I wanted to focus on the scientific and historical aspects of the works.
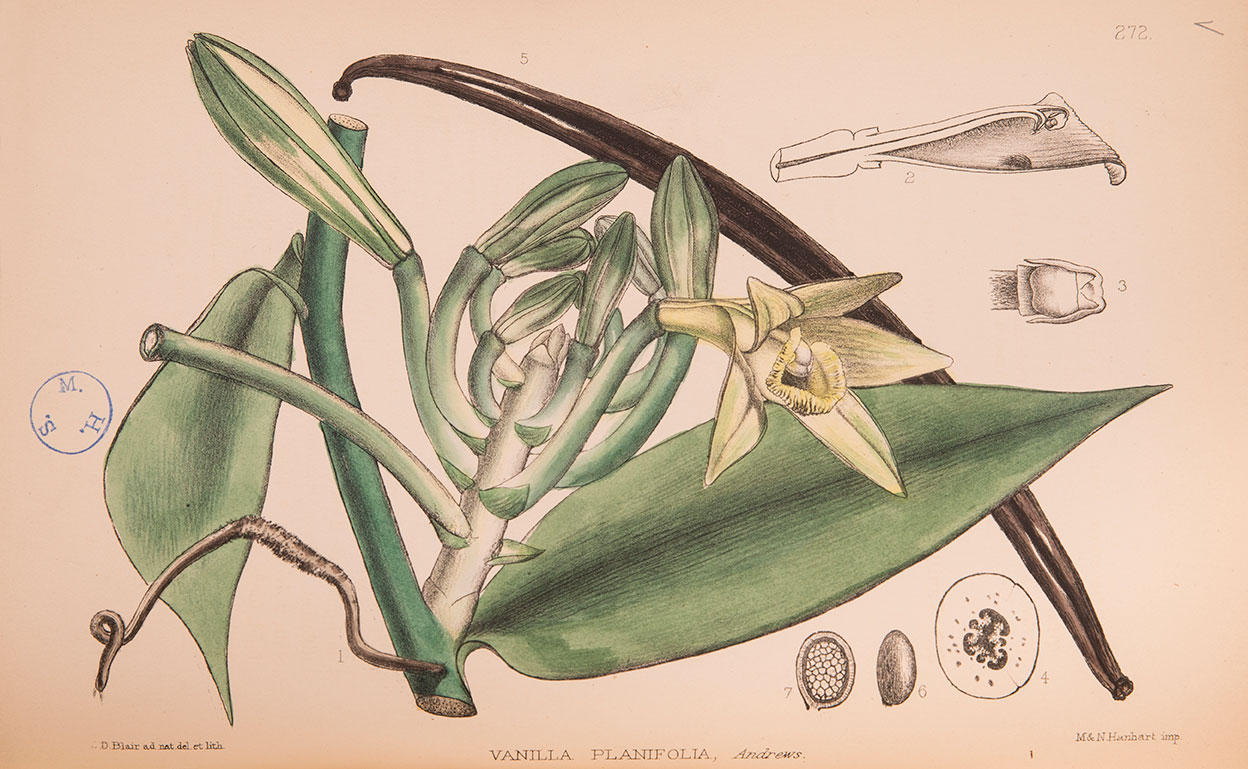
Displayed in the first case of Asian Orchids Illustrated is a rare 1874 volume of Japanese physician Yokusai Iinuma’s botanical encyclopedic compendium, Shintei Somoku Zusetsu. It features a partially hand-colored illustration of the orchid Cypripedium japonicum, which can be found in China, Japan, and Korea. The plant has been used in China to treat malaria, snake bites, and lower back pain.
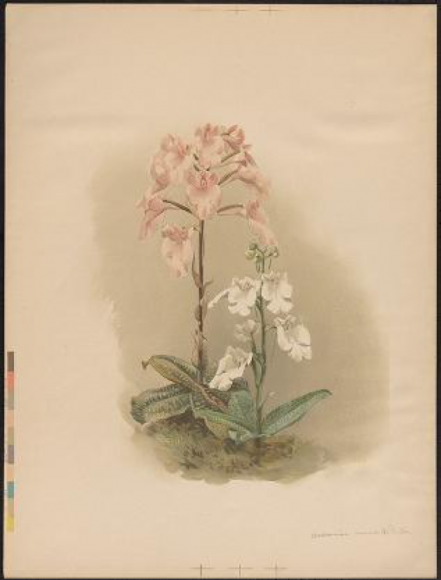
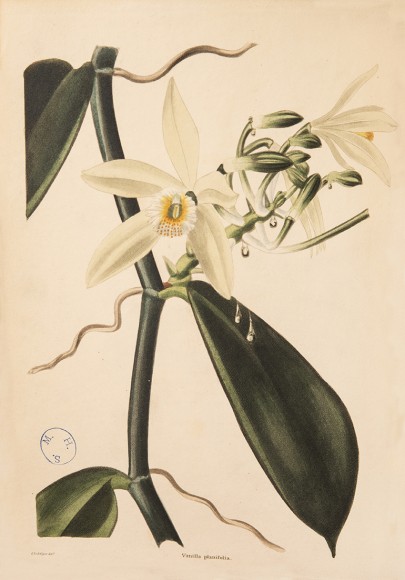
Also featured are three oversized tomes of the Annals of the Royal Botanical Garden, Calcutta, featuring partially hand-colored orchid plates by Indian artists and lithographers. The orchids featured in this case are Dendrobium densiflorum; the leaves are ground into a paste and used for bone-setting in India, and Goodyera biflora, which is used for tuberculosis, as an anti-inflammatory, and for snake bites.
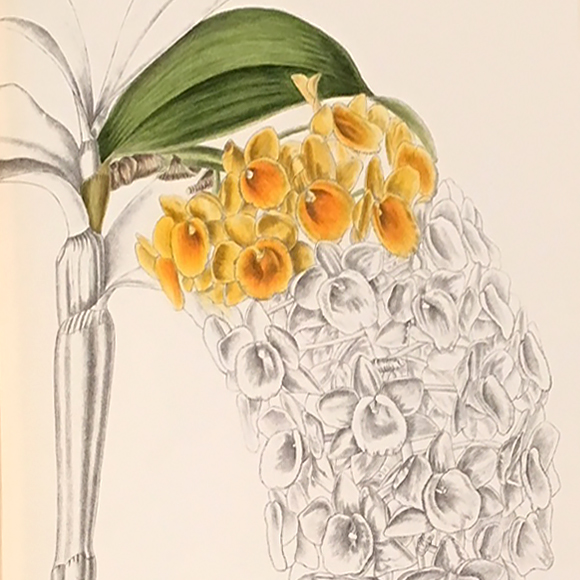

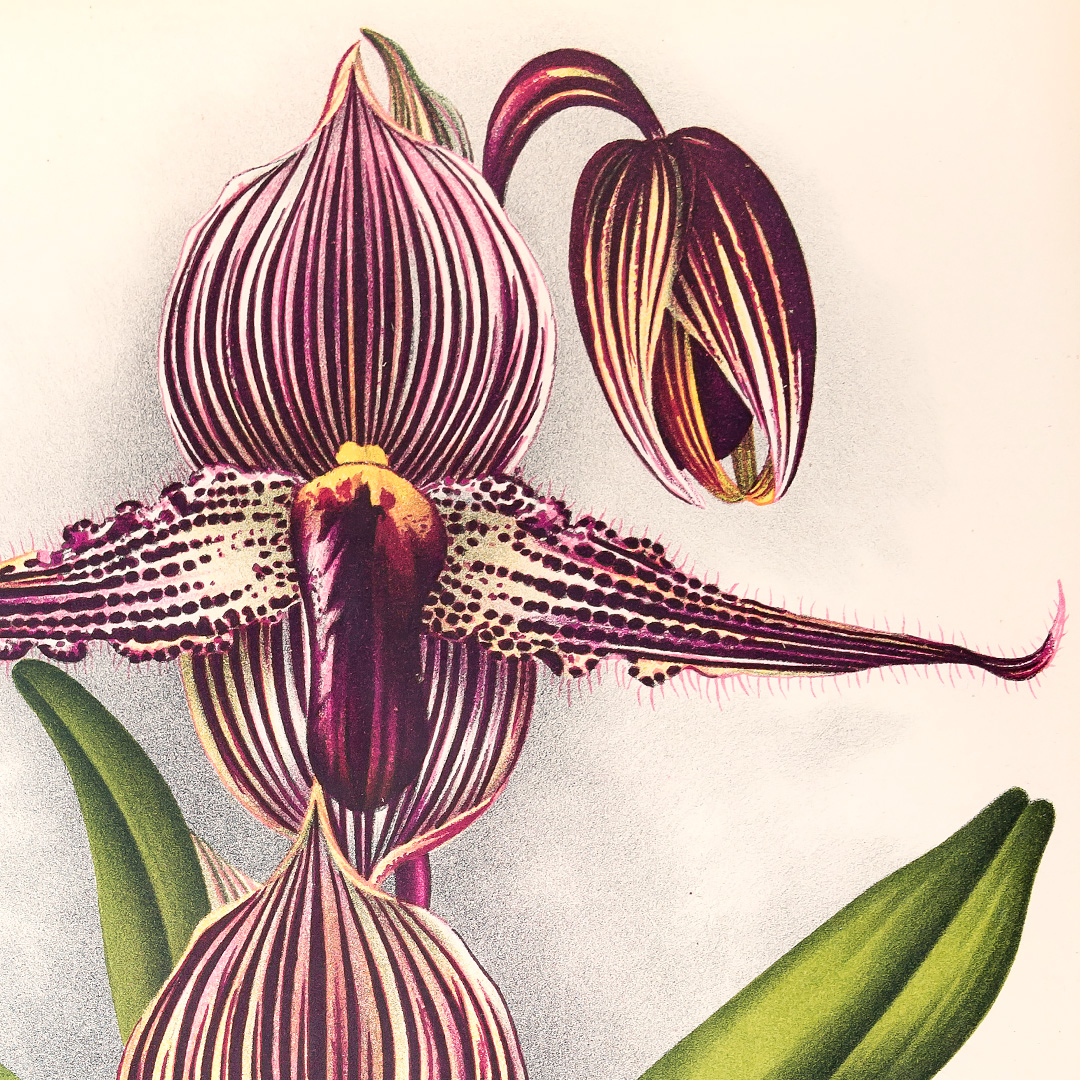
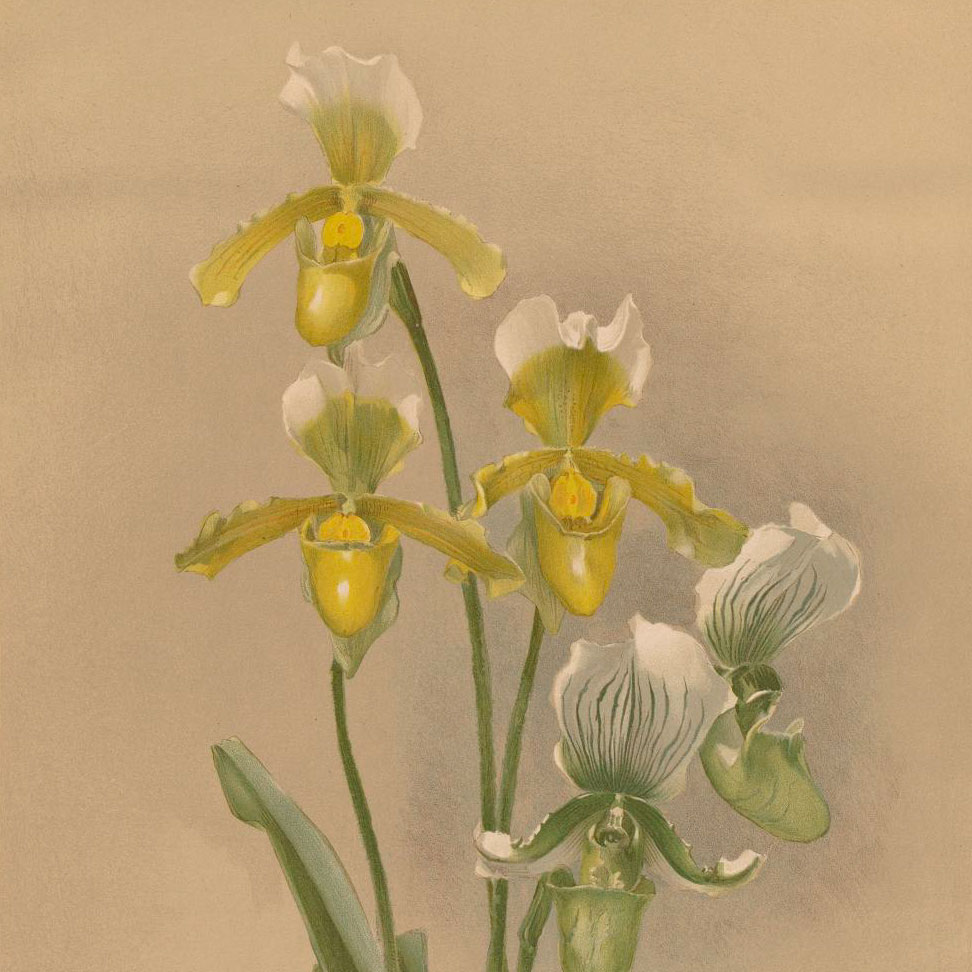
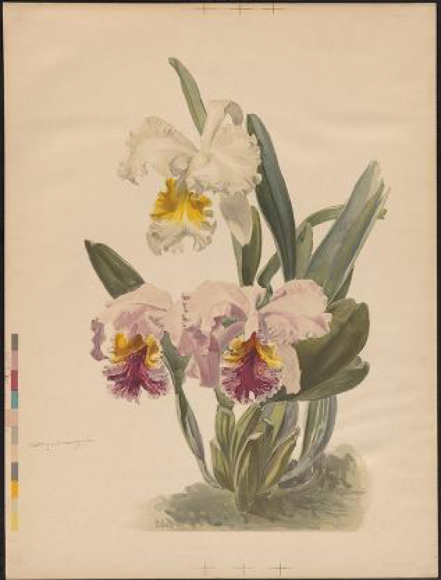
And finally, the third case contains six different volumes showcasing the interesting history of the Rothschild slipper orchid, often claimed to be one of the most expensive and sought-after orchids of our time. This poor orchid has been through the proverbial ringer, so to speak. Not only has it had its name changed without being consulted, from Cypripedium Rothschildiana to Paphiopedilum Rothschildianum, but it has been often mistaken for other species of orchids, has been misrepresented by collectors, and has had its bloom time genetically modified. Lastly, but most importantly, it has been to the brink of extinction. On display at the Orchid Show is a hybrid Paphiopedilum that’s related to the Rothschild’s slipper orchid.
On Sunday, February 25, and Tuesday, February 27, the Lenhardt Library hosts a free talk at 2 p.m. about these extraordinary books that contain orchidaceous history on their beautifully illustrated and typeset pages. After the talk, you will be invited to view a few more “orchid-delectables” in the library’s Rare Book Room.
©2018 Chicago Botanic Garden and my.chicagobotanic.org